Quiz time? Use These Built-in Question Types in Storyline – Part 2

In my last blog (if you haven’t read it, head over here), we saw five of the eleven graded question types that Articulate Storyline offers:
- True/False
- Multiple Choice
- Multiple Response
- Fill in the Blank
- Word Bank
I promised you we’ll look at the rest of the lot in another blog. So, here I am. Without wasting too many words, let’s get on with it.
Drag and Drop
If you are somebody who has experience copying/moving files to and from folders using a computer, then you already know what drag and drop means. In Storyline, there are two kinds of drag and drop question types:
- Matching drag and drop
- Sequencing drag and drop
6. Matching Drag and Drop
In a typical Drag and Drop question type, the learner is asked to move an image or a highlighted text box to another part of the screen i.e., he moves the text box from the match column and drops it in the choice column, using the mouse.
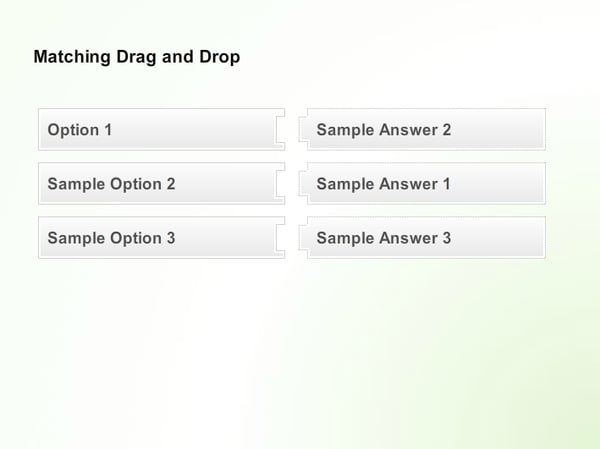
Gone are the days when you had to do heavy programming to add a drag and drop interaction to your e-learning courses. If you’d like to learn how to customize a matching drag and drop, check out this informative blog written by one of our developers.
7. Sequencing Drag and Drop
This is a little different from matching drag and drop. Although both types require the chosen option to be dragged and dropped, a sequencing drag and drop is an interactive sorting question used to test the learner’s ability to identify and sort events in the correct sequence.
Here’s an example.
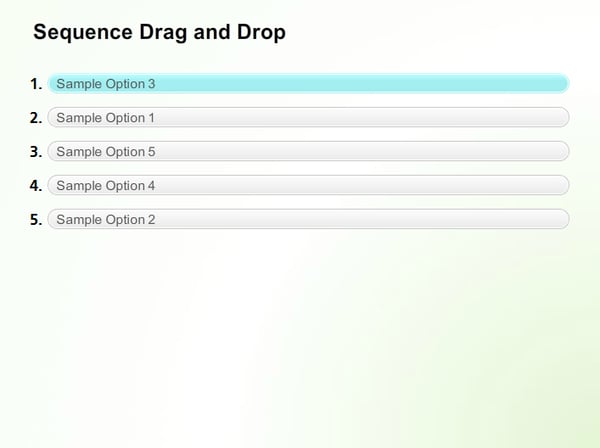
Note: You can use up to 10 matching pairs in both matching and sequencing drag and drop graded questions, and the learner must match all the elements in the match column to the ones in the choice column for the question to be graded as correct.
Bonus Tip: It’s a good practice to combine characters with drag and drop interactions in your online learning courses. Instead of simply having a character/avatar offering your learners straightforward tips, you can encourage your learners to interact with the screen by dragging an object over the character/avatar to trigger their (read: object’s) response. (Just saying!)
Drop-Down
Drop-down menus are a great idea if there’s anywhere between 10-15 options in the choice menu. You can put a healthy amount of information in your drop-down menu without cluttering the entire page, because the list’s options are hidden when the learner doesn’t need them.
Just like Drag and Drop, two types of Drop-Down are available in Storyline:
- Matching Drop-Down
- Sequencing Drop-Down
8. Matching Drop-Down
In a matching drop-down graded question, the learner must select items from the drop-down menu to match the items in the first column.
Here’s an example.
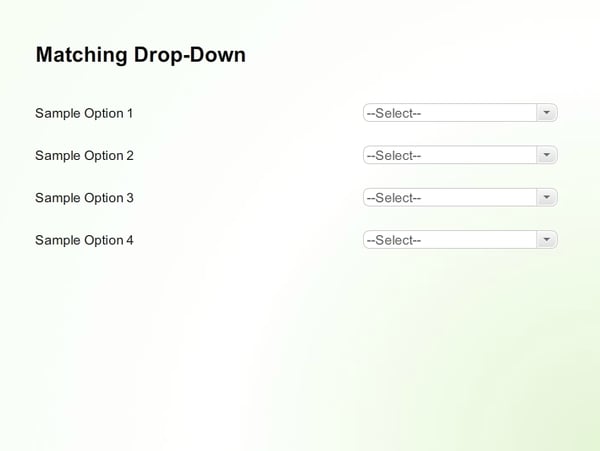
9. Sequencing Drop Down
Similar to matching drag and drop, a sequencing drop-down graded question requires the learner to choose the item from the drop-down menu to arrange it in a sequence.
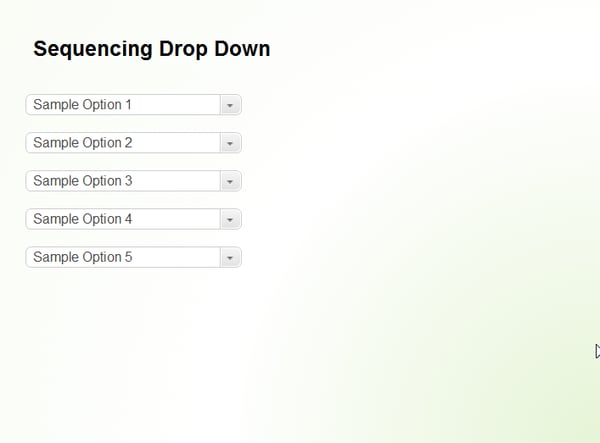
Note: Both matching and sequencing drop-down graded questions allow a maximum of 10 match and sequence items respectively.
When drop-down lists grow larger than 15 options, they become difficult to scan and navigate. An example of this is the country selector which contains more than 100 options, making it almost impossible to get a good review. So, keep the number of options as low as possible to allow the learner to find the option they are looking for.
10. Numeric
A numeric graded question is a question which asks the learner to answer using, well, numeric values (1 2 3 4 …). Numeric entry questions can be used when, for example, you want learners to calculate the click-through rate of an ad, based on the number of clicks and views. Here’s how it would look.
Some of the questions may require answers with decimal points (e.g. 14.678 or 0.12). Storyline gives you the ability to convert numerical values to the decimal format. Here’s how.
Note: In a numeric graded question, the learner is restricted to answering using only numbers.
11. Hotspot
Here’s how a hotspot question works: you present learners with an image, and to respond, learners must mark a place on that image. There are no visible clues (unless you choose to put them into the image itself), and learners must know which part of the image to select, without any guidance.

Storyline has long been regarded as one of the best authoring tools for e-learning development, and undoubtedly, it’s an important tool when it comes to being user-friendly and the amount of features it offers. It offers simple, yet useful quiz templates that make it a worthy candidate for creating e-learning assessments. Make use of its built-in question types and guarantee your learners a rich, attractive, and engaging learning experience.





![A Quick Round Up About eLearning Rapid Authoring Tools [Infographics]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hubfs/Imported_Blog_Media/convert-ppt-to-elearning-with-lectora.jpg)