Empowering Pharma Representatives — eLearning Meets Sales Enablement Training

In sales, keeping up with the fast pace is so important, especially if you're aiming to stay ahead. Sure, everyone in sales understands that you need to keep your product knowledge up-to-date, but for those in the pharmaceutical sector, it's a whole different game. Imagine the challenges they face—new drugs, regulations, and scientific advancements—it's a lot to handle!
That's where sales enablement training becomes a game-changer. This training isn't just about knowing your product, it's about arming pharmaceutical sales pros with the right tools and insights to really make a mark in their challenging field.
→ Download Now: Microlearning — Where Does It Fit in Your Learning Strategy?
Table of Contents
- What is Sales Enablement?
- Why is Sales Enablement Important in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
- How to Design an Effective Sales Enablement Training Program?
- How to Ensure Continuous Reinforcement for Sales Representatives?
What is Sales Enablement Training?
Sales enablement training equips sales teams with a comprehensive suite of tools, resources, and skills essential for successfully engaging buyers. This training goes beyond basic sales techniques by providing strategic insights into buyer behavior, personalized communication strategies, and the ability to leverage data-driven decision-making. It empowers sales professionals to navigate complex sales processes, tailor their approaches to different customer needs, and ultimately close deals more efficiently. By fostering a deeper understanding of the sales cycle and enhancing adaptability, such training becomes a vital asset in achieving sustained success in competitive markets.
Want to level-up your sales enablement strategies? Unveil the secrets with this infographic!
Wondering how to improve sales performance with enablement for pharma sales representatives? Continue reading!
Why is Sales Enablement Important in the Pharmaceutical Sector?
In the fast-paced world of pharmaceuticals, where understanding intricate details about medications and adhering to stringent regulatory standards are paramount, sales enablement takes on a critical role. The sector demands a deep comprehension of complex products and the ability to effectively communicate their value to healthcare professionals. Imagine a team of sales representatives equipped not only with in-depth knowledge of their products but also with the confidence to engage meaningfully in discussions, navigate challenges, and address the unique needs of their audience. This foundational preparation sets the stage for a sophisticated and strategic approach to selling in an industry where expertise and trust are key. As the pharmaceutical landscape continues to evolve with new innovations and regulations, equipping sales teams with the right tools and insights becomes more crucial than ever.
The pharmaceutical sector presents various unique challenges for sales reps, thus emphasizing the need for sales enablement training. Some of the challenges are listed below:
1. Complex Products and Services:
Pharmaceutical products and processes often involve a thorough understanding of the scientific concepts and components. Sales enablement ensures representatives have a proper understanding of the products, allowing them to effectively communicate benefits, mechanisms, and usage to healthcare professionals.
2. Regulatory Compliance:
The pharmaceutical industry is highly regulated, and sales representatives must adhere to strict guidelines. Sales enablement training helps ensure that the sales representatives understand these regulations and are able to communicate within legal and ethical boundaries.
3. Evolving Market Landscape:
As the pharmaceutical industry is constantly evolving with new products, innovations, equipment, treatments, and competitors, pharma sales training ensures the representatives stay up-to-date with the latest developments. It ensures that they can effectively position the products and respond to market changes.
4. Targeted Communication:
Sales representatives in the pharma sector deal with a diverse audience. It ranges from doctors to nurses to hospital administration. With that said, it’s important to keep in mind that the healthcare professionals are busy people. Therefore, providing them with relevant, concise information works the best. Sales enablement strategies equips reps with the techniques and tools to deliver targeted, impactful messages that resonate with their audience and translate into results.
5. Enhanced Customer Relationships:
When dealing in the pharmaceutical sector, building trust with healthcare professionals is crucial. So, sales enablement training not only comes in handy for delivering information on particular products and the science associated with them but can also be used to help sales representatives develop soft skills. It ensures the skills and knowledge to build strong, long-lasting relationships, fostering loyalty and repeat business.

Where Does Microlearning Fit in Your Learning Strategy?
Uncover the Secrets to Crafting High-performing Micro Assets!
- What Microlearning is and What it is NOT?
- Types of Microlearning Assets
- Tips and Tools for Rapid Microlearning Development
- And More!
What to Include in Comprehensive Sales Enablement Training for Pharma Reps and How to Use eLearning Solutions?
Your Sales Team Must be Dynamic, Knowledgeable, and Up to date!
Here are 5 types of training that make for an exhaustive sales enablement training curriculum:
- Human anatomy and physiology
- Diseases and symptoms
- Drugs for treatment
- Sales process
- Handling objections
Continue reading to know the details about each type of training.
Here are the five types of training that must be covered in the exhaustive sales enablement training curriculum and how to leverage eLearning for it.
1. Human Anatomy & Physiology
This type of training provides a thorough understanding of human anatomy and physiology. Sales representatives learn about the functions of various organs, their structures, and what occurs when these organs function abnormally. Such knowledge is crucial for understanding how drugs interact with the body. Training on human anatomy and physiology is often delivered by medical professionals, such as doctors.
Utilize eLearning solutions to deliver interactive modules on human anatomy and physiology. Incorporate videos, and quizzes for engaging learning experiences. Offer virtual sessions with medical professionals for deeper insights and provide accessible resources for self-paced learning.
2. Diseases and Symptoms
In this training, sales representatives learn about various diseases that their company’s medications treat. They gain insight into disease symptoms, causes, progression, and advancements in treatment. This knowledge equips them to communicate the benefits of the company’s drugs to healthcare professionals effectively.
Offer eLearning courses to deliver comprehensive modules on diseases and symptoms. Sales representatives can engage with interactive content and simulations to understand the diseases targeted by the company's medications, including symptoms, causes, progression, and treatment developments. This approach enhances reps' ability to convey drug benefits to healthcare professionals while offering an engaging and flexible learning experience.
3. Drugs for Treatment
As the name suggests, this particular training focuses on providing sales representatives with detailed information about various drugs available for each disease and their compositions.
To leverage eLearning for drugs for treatment training, organizations can create interactive online modules that provide detailed information about various drugs and their compositions. These modules can include multimedia elements such as videos and animations to explain how the drugs work, their indications, and contraindications. Incorporating quizzes and assessments can help reinforce knowledge and ensure sales representatives understand the material thoroughly. Additionally, virtual simulations can mimic real-life scenarios, allowing representatives to practice answering technical questions from healthcare professionals.
4. Sales Process
After completing their medical training, sales representatives move on to learning the sales process. This includes strategies for initiating conversations with doctors, introducing the drugs, and promoting both the drug and the company.
Additionally, eLearning platforms can offer comprehensive training on essential soft skills like communication techniques and relationship-building strategies. Senior sales trainers can provide virtual mentorship and feedback, ensuring effective interactions with healthcare professionals are achieved.
5. Handling Objections
Finally, healthcare sales representatives are trained on how to handle the doctors’ objections. They learn techniques for responding to concerns and questions in a respectful and professional manner. This training helps ensure that representatives can maintain positive relationships with healthcare professionals while addressing any hesitations they may have about the medication.
Once the training is complete, sales representatives are ready to work with doctors and promote your company’s drugs.
Effective eLearning solutions can be the backbone of high-impact sales enablement training!
How to Design an Effective Sales Enablement Training Program?
1. Assess the Specific Needs of Pharma Representatives:
Identify the unique challenges and requirements that pharmaceutical sales representatives face. Consider factors such as diverse product portfolios, complex regulatory environments, and the necessity for in-depth scientific knowledge. Conduct surveys or interviews to gather insights directly from the reps to tailor the training program effectively.
2. Define Clear Objectives for the Training Program:
Establish specific, measurable goals that the training program should achieve. This could include improving sales numbers, enhancing product knowledge, increasing customer engagement, or ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Clear objectives will guide the training content and help measure its effectiveness.
3. Create Engaging and Relevant Training Content:
Develop training materials that are directly applicable to the reps' day-to-day activities. Use real-world scenarios, case studies, and examples that the reps can relate to. Ensure the content is not only informative but also engaging, using multimedia elements like videos, animations, and interactive modules to keep participants interested.

Where Does Microlearning Fit in Your Learning Strategy?
Uncover the Secrets to Crafting High-performing Micro Assets!
- What Microlearning is and What it is NOT?
- Types of Microlearning Assets
- Tips and Tools for Rapid Microlearning Development
- And More!
4. Incorporate Interactive and Practical Learning Techniques:
Facilitate active learning by including role-playing exercises, simulations, and workshops that mirror real-life sales situations. Encourage peer-to-peer learning and discussions to foster collaboration and knowledge-sharing among reps. Hands-on practice will help reps apply what they’ve learned more effectively.
5. Provide Ongoing Support and Resources:
Offer continuous access to a library of resources such as product information, industry trends, and sales strategies. Implement a mentorship program where experienced reps can provide guidance and support to newer reps. Ensure that reps have access to experts who can answer questions and provide additional insights when needed.
6. Implement Regular Assessments and Feedback Loops:
Regularly evaluate the reps' progress through quizzes, assessments, and performance reviews. Use these evaluations to identify areas where reps may need additional support or training. Establish feedback mechanisms where reps can provide input on the training program, allowing for continuous improvement and adaptation.
7. Continuously Update the Program to Align with Industry Changes:
Stay informed about the latest developments in the pharmaceutical industry, including new products, regulations, and sales techniques. Regularly revise the training content to ensure it reflects current industry practices and knowledge. Encourage reps to stay up-to-date by incorporating these updates into the program.
Watch this video to explore 5 easy steps to design an effective sales enablement training program.
This extensive sales enablement coaching should be supported by continuous reinforcement so that the sales representatives are always productive. And how can you do so? Well, with technology by your side, learning can be imparted on the go with just a click.
How to Ensure Continuous Reinforcement for Sales Representatives?
- Schedule regular one-on-one feedback sessions to discuss performance and areas for improvement.
- Implement a mentorship program pairing new reps with experienced colleagues.
- Use sales performance metrics to set clear, achievable goals.
- Provide ongoing training sessions focused on developing sales techniques and product knowledge.
- Offer incentives or bonuses for meeting or exceeding sales targets.
- Create a platform for sharing success stories and best practices among the team.
- Utilize role-playing exercises to practice handling objections and closing deals.
- Encourage participation in industry conferences and workshops for networking and learning.
- Foster a supportive team environment that celebrates individual and group achievements.
- Regularly update the team on market trends and company developments to keep them informed and motivated.
Reinforcing Sales Skills Nonstop with Microlearning!
When it comes to ensuring quick, continuous learning and reinforcement for your sales representatives, microlearning for sales training is worth a shot!
In the fast-paced world of sales, where staying updated and sharp is crucial, microlearning emerges as a powerful tool for ensuring quick and ongoing learning for sales representatives. By leveraging microlearning strategies, organizations can provide their sales teams with concise, targeted learning experiences that focus on key aspects of their roles.
Imagine equipping your sales representatives with bite-sized microlearning nuggets that cover essential topics, such as product knowledge, sales techniques, customer relationship management, and industry trends. These microlearning modules, designed to be mobile-friendly and responsive, offer unparalleled flexibility. Sales representatives can access them at their convenience— whether on the go, between meetings, or during their daily commute.
The true advantage of microlearning lies in its adaptability. These microlearning modules serve as ready reckoners, allowing sales representatives to refresh their knowledge or gain new insights exactly when needed. Before engaging with a healthcare professional or any client, they can quickly review relevant information, ensuring they are well-prepared and confident.
Furthermore, the continuous reinforcement provided by microlearning fosters a culture of learning within the sales team. It encourages proactive engagement with training materials, leading to better retention of information and improved sales performance. By making learning an integral part of their daily routine, sales representatives can maintain a competitive edge in a constantly evolving market.
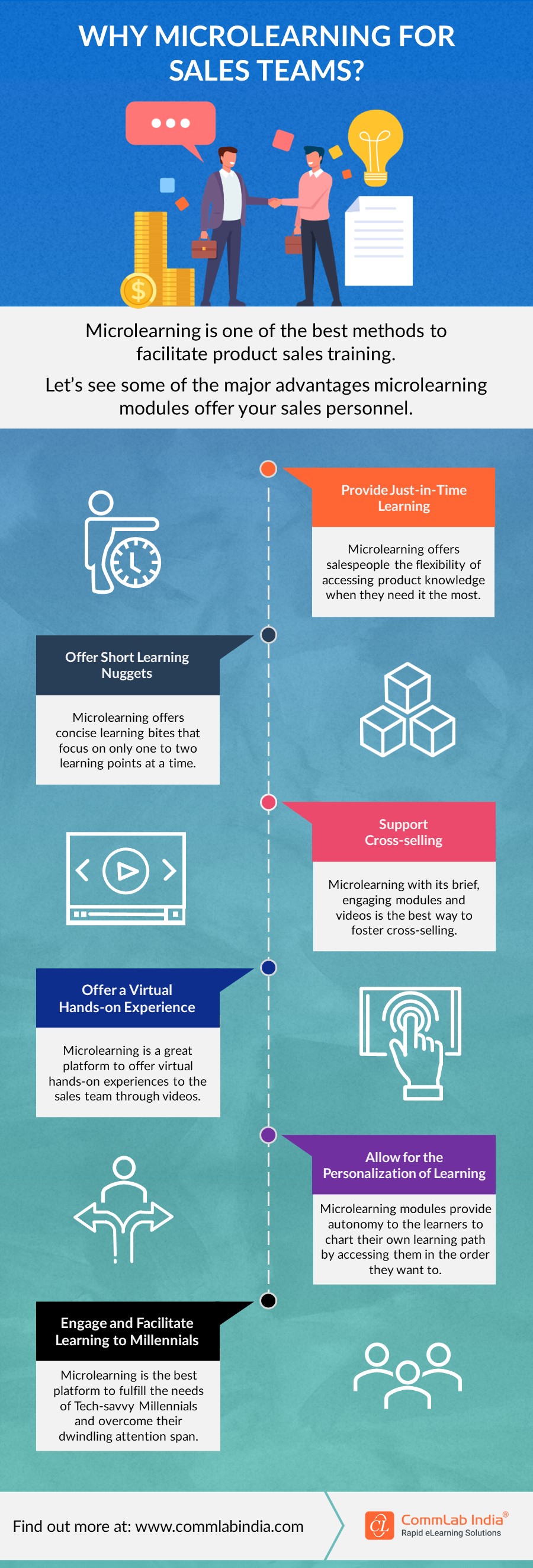
Have a look at this infographic to understand why microlearning is an ideal choice for training sales teams.
Parting Thoughts!
In the competitive world of pharmaceutical sales, success is directly proportional to the sales representative’s ability to deliver clear, impactful information to healthcare professionals. To polish these skills of sales representatives and equip them with relevant, useful information, sales enablement training proves beneficial. However, one-time training won’t do your sales representatives any good. You need to provide them with regular updates and advancements happening in the pharmaceutical world.
Although pharmaceutical sales are very tough, it can be made easy if you give the sales team the edge of accessing training on the go! That’s the magic of microlearning in sales enablement training. If you wish to explore more on where does microlearning fit into your learning strategy, we’ve got just the right eBook for you. Check it out below!





![4 Ways to Create Microlearning for your Sales Training [Infographic]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hubfs/Imported_Blog_Media/microlearning-for-sales-training-infographic.png)
