Elements of Storyboards for Designing Interactive E-Learning

From desktops to mobiles, e-learning has come a long way and gained a lot of popularity. But what’s the secret to creating impactful e-learning courses? It all starts with a well-designed storyboard.
A storyboard serves as the blueprint for your online course, weaving together video, text, audio, visuals, and interactive elements to enhance the core message and captivate learners. These components work in harmony to create a seamless and engaging learning experience.
→ Download Now: Instructional Design 101
More than just a plan, a great storyboard acts as a bridge between your course concept and the final product. It aligns instructional designers, subject matter experts (SMEs), developers, and stakeholders around a unified vision. This shared understanding minimizes confusion, fosters collaboration, and ensures your ideas come to life with precision and purpose.
Clarity and accuracy are paramount in a storyboard, making it easy for clients, editors, and production teams to grasp and execute the vision. As David Becker, Principal Consultant at Becker Consulting, aptly puts it: “The storyboard’s primary value is that it forces you to have a reason for and a consistent approach to everything you do.”
Given that a well-written storyboard is a critical component of creating superior quality eLearning courses, here are a few important elements you need to consider at the storyboard level:
- Learning objectives
- A brief description of the course navigation
- A detailed description of how interactions should be designed
- Instructional design strategies to guide learners
- Information on audio cues such as music or sound effects along with file names
- A proper format that arranges the lessons or topics
- Accurate feedback for assessments
A storyboard template usually contains basic areas such as:
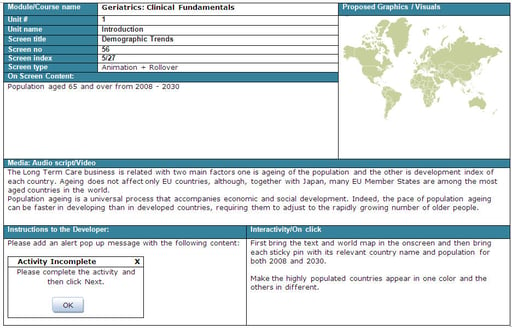
- Title: This area usually contains the name of a unit, topic, or module.
- Screen Number: Signifies the number of the screens or slides in the course.
- Proposed Graphics/Visuals: Visuals, graphics, video clips, etc. are shown in this area. Text can also be included here.
- Audio: Audio scripts, name of music files, sound effects, etc. are included in this area.
- Interaction Area: This area describes the interactions on each screen. A wide variety of activities can be provided.
Given below are some additional tips to be kept in mind while developing an e-learning storyboard:
- Make the storyboard learner-centric. This might sound simplistic, but many instructional designers sometimes lose track of this simple fact. Always keep the learner in mind.
- Ensure that an effective instructional strategy is applied globally throughout the course.
- Content flow and the final quiz need to be aligned with the learning objectives.
- Structured learning objectives must help the learner understand the course.
- Ensure the screen is not cluttered excessively with graphics and content.
Developing a well-crafted storyboard is critical to the development of an effective e-learning course. By having a storyboard, you communicate your visualization ideas to courseware developers and clients and also create a blueprint of what your course will look like. Incorporating instructional design strategies and instructional design models into your storyboard ensures an effective and engaging learning experience. Storyboards are important – use them well!


![E-learning Development: 6 Benefits of Using Storyboards [Infographic] E-learning Development: 6 Benefits of Using Storyboards [Infographic]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Imported_Blog_Media/storyboards-elearning-development-infographic.png?width=650&height=1100&name=storyboards-elearning-development-infographic.png)


![How to Tackle eLearning Implementation Challenges? – Rapid eLearning to Save the Day [VIDEO]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hubfs/Imported_Blog_Media/How-to-Tackle-eLearning-Implementation-Challenges-%E2%80%93-Rapid-eLearning-to-Save-the-Day-VIDEO.jpg)
