Experiential Learning in eLearning – The Secret to Meeting Business Goals

As Learning and Development (L&D) Managers and Training Managers, we are acutely aware that our workforce is shaped not just by traditional training but predominantly by their experiences. In a corporate environment, where adaptability and practical application are crucial, experiential learning emerges as a powerful approach to development. And custom eLearning courses can help offer experiential learning.
The wisdom, clarity, and insights gained from real-world experiences cannot be rivaled by textbook knowledge or formal training alone. This is where David A. Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory comes into play, providing a framework that highlights the importance of learning through experience.
→ Download Template: Align Training with Business Goals for Max Impact and ROI
About Experiential Learning
Kolb's theory, formulated in 1984, emphasizes that adults learn best when they engage in a cycle of experiencing, reflecting, thinking, and acting. This cycle encourages learners to draw meaning from their experiences, allowing them to apply their insights to future situations.
In the context of corporate training, this means that employees are more likely to retain information and develop skills when they are actively involved in the learning process, rather than passively receiving information through lectures or reading materials.
Table of Contents
- About Experiential Learning
- What is the Experiential Learning Theory?
- Why Conventional eLearning Fails in Incorporating Experiential Learning
- Addressing Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory with eLearning
- 4 Immersive Ways to Design Experiential eLearning
- Experiential Learning and Business Goals
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Incorporating experiential learning into corporate training has manifold benefits. Firstly, it fosters deeper engagement among learners. When employees can relate their learning to real-life situations, they become more invested in the training process. This leads to enhanced motivation and a better understanding of the material, resulting in improved performance on the job.
Moreover, experiential learning cultivates critical soft skills that are essential in today’s workplace. Skills such as problem-solving, teamwork, and effective communication are often best developed through hands-on experiences rather than theoretical discussions.
Simulating real business scenarios or allowing employees to tackle projects that require collaboration and innovation, will help L&D managers create rich learning environments where these skills naturally flourish.
How Can eLearning Support Experiential Learning?
- Concrete Experience – Scenarios, Videos
- Reflective Observation – Case Studies
- Abstract Conceptualization – Mind maps and animations
- Active Experimentation – Gamification
Additionally, the adaptive nature of experiential learning aligns perfectly with the dynamic demands of modern business. As organizations evolve, so do the skills required to succeed. By implementing experiential learning approaches, training programs can be designed to be more flexible and responsive to the changing landscape. This adaptability equips employees with relevant skills and empowers them to drive their learning.
However, the challenge arises: how can we effectively emulate experiential learning in eLearning? Virtual simulations, interactive case studies, and collaborative projects can mimic real-world scenarios, allowing learners to practice and apply their skills in a safe space.
As L&D and Training Managers, embracing the principles of Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory and integrating them into our training programs can dramatically enhance the learning experience.
What is the Experiential Learning Theory?
David A. Kolb defines experiential learning as “the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience. Knowledge results from the combination of grasping and transforming experience.”
The theory also reveals the cyclic nature of experiential learning and how it takes place in four stages. Although presented in the continuum, the stages can occur in any order.
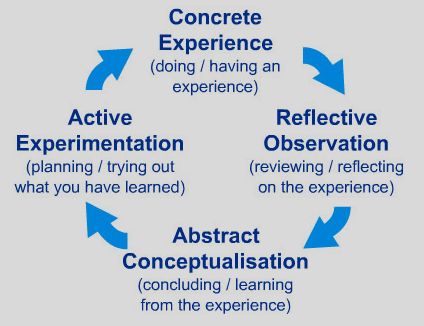
The cycle begins with the experience learners might have had, which is followed by a chance to reflect on that experience. Moving on, learners conceptualize and derive conclusions about what they’ve observed, which leads them to experiment with different behaviors.
Concrete Experience: This is the initial phase where the learner encounters a new experience or reinterprets an existing one. It's the foundation of the learning process, as it provides the raw material that participants can later reflect upon and analyze.
Reflective Observation: In this stage, learners take time to reflect on their experiences. This reflection process involves observing and considering different perspectives to better understand the occurrence and the reactions it provoked.
Abstract Conceptualization: Here, learners develop theories, models, or hypotheses based on their reflections. They synthesize information and form generalizations that can be used to anticipate and understand future situations.
Active Experimentation: The final stage involves applying newly formed concepts and hypotheses through practical action. Learners try out what they've learned in real-world settings, leading to more experiences, which, in turn, fuel the cycle anew.
Why Conventional eLearning Fails in Incorporating Experiential Learning
Do your conventional eLearning courses provide scope for experimentation? Are they aimed at disseminating information pertaining to different learning needs? They might be filled with definitions and concepts. However, do you think memorizing information is sufficient? Don’t you want learners to apply the acquired knowledge and perform their jobs efficiently?
To affirm this, here’s a diagram that denotes the difference between knowledge in isolation and knowledge in experimental learning.
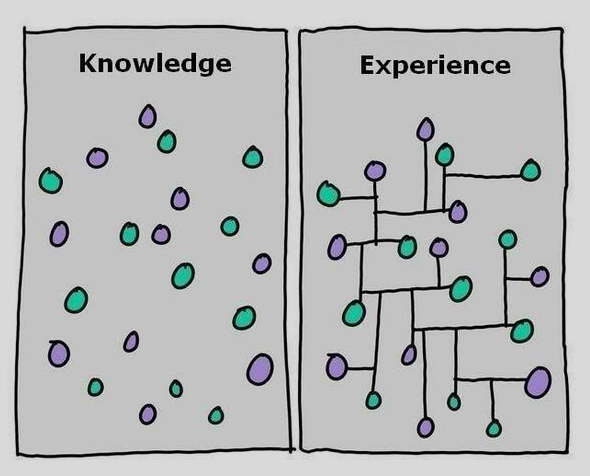
Image Source: Buffer
As evident, knowledge only helps when learners are able to make connections among what they know. And true knowledge seldom happens without experience.
What Are the Benefits of Experiential Learning in eLearning?
Experiential learning in corporate training offers a wealth of benefits that significantly enhance the learning experience for adults. Here are some key advantages:
1. Active Engagement
Experiential learning fosters active participation, allowing employees to dive deep into the material. This hands-on engagement cultivates a deeper understanding of concepts, transforming learners from passive recipients into active participants in their professional development.
2. Real-World Application
One of the standout benefits of experiential learning is its emphasis on real-world relevance. By simulating workplace scenarios or engaging in project-based tasks, employees can see the direct impact of their training on their daily work. This approach helps bridge the gap between theory and practice, making the learning experience more applicable.
3. Enhanced Retention
Research indicates that adults retain information more effectively when they can apply what they’ve learned in practical situations. Experiential learning promotes long-term retention by allowing employees to practice skills and concepts, resulting in a robust understanding that is more likely to endure.
4. Development of Critical Thinking Skills
Engaging in experiential learning sharpens critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. As employees navigate challenges and make decisions in realistic environments, they hone the analytical skills necessary to tackle complex scenarios in their roles, a crucial asset in any corporate setting.
5. Collaboration and Communication
Many experiential learning activities encourage teamwork among participants, enhancing collaboration and communication skills. Working together on projects or in discussions allows employees to learn how to share ideas, provide and receive feedback, and build valuable professional relationships.

Align Training with Business Goals
Editable Questionnaire to Help You Make the Right Choice!
- Identify organizational goals
- Check what your people need to do achieve those goals
- Identify SMART learning objectives to fill performance gaps
- Design for impact
6. Self-Directed Learning
Experiential learning empowers employees to take ownership of their professional growth. By encouraging exploration and inquiry, it enables learners to pursue their interests and goals, resulting in a more personalized and motivating training experience.
7. Immediate Feedback
A well-structured experiential learning environment provides immediate feedback, allowing employees to identify their strengths and areas for improvement in real time. This instant assessment facilitates timely adjustments and reinforces the learning process.
In summary, experiential learning in corporate training not only boosts engagement but also emphasizes real-world application, retention, critical thinking, collaboration, self-directed learning, and timely feedback. These advantages contribute to a richer and more effective training experience, equipping adult learners with the skills and knowledge necessary for success in their careers.
Addressing Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory with eLearning
Let’s now delve into how eLearning can address each phase of Kolb's theory.
Concrete Experience
Custom eLearning solutions support diverse formats to engage learners in the Concrete Experience phase. Virtual reality simulations and interactive scenarios allow learners to encounter new experiences in a controlled and safe environment. These platforms can create immersive experiences, enabling learners to face real-world challenges without the risks associated with actual experimentation.
Incorporating multimedia elements such as videos and podcasts can also depict real-life situations, offering learners a sensory-rich introduction to new concepts or challenges. Modular course formats can further personalize learning journeys, allowing learners to select experiences most relevant to their roles.
Reflective Observation
eLearning modules support Reflective Observation by integrating assessments and real-life branching scenarios. For instance, scenario-based assessments allow learners to apply concepts in practical situations, prompting them to reflect on their decisions and outcomes.
Interactive discussion boards and peer feedback encourage dialogue, helping learners to evaluate different perspectives. Additionally, guided reflections through quizzes or prompts focus attention on key experiences, enhancing critical thinking about their learning journey. These features collectively foster a deeper understanding of their experiences and reactions.
Abstract Conceptualization
eLearning courses play a vital role in supporting the Abstract Conceptualization phase by providing tools such as mind maps and animations. Mind mapping software enables learners to visually organize their thoughts and synthesize information, making it easier to form generalizations and hypotheses.
Additionally, animations can illustrate complex concepts dynamically, helping learners grasp abstract ideas more effectively. Interactive modules with case studies and problem-solving exercises encourage deeper understanding and facilitate the creation of models or frameworks based on insights gained.
With access to curated databases and digital libraries, eLearning further enriches this phase by offering diverse resources for learners to reference as they develop their theories.
Active Experimentation
In the Active Experimentation phase, eLearning facilitates the application of new knowledge through practical assignments and projects. Simulations and role-playing exercises are particularly effective, allowing learners to test their hypotheses in virtual settings.
Bespoke eLearning can offer scenario-based learning and gamification where learners can work through various potential real-world situations and adjust their responses based on feedback. By incorporating challenges and missions that mimic workplace dynamics, learners are encouraged to apply their knowledge actively and iterate on their approaches in real time.
Automated assessments and instant feedback mechanisms ensure that learners receive immediate insights into their performance, promoting continuous improvement and reinforcing the learning cycle.
Integrating Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory into eLearning not only creates a holistic learning environment but also ensures that each phase of the learning cycle is addressed and optimized for an engaging, effective educational experience.
4 Immersive Ways to Design Experiential eLearning
1. Go Beyond Traditional Training with Online Simulations
Adult learners gather and process information using their senses; however, it is only by “doing” that they actually learn – the crux of experiential learning. eLearning simulations allow learners to experiment with situations close to the real work environments of learners, paving the way to “doing and learning.”
Active doing and experimentation in eLearning simulations allow learners to apply their knowledge in different scenarios and situations. For instance, application training, such as software requires “hands-on practice” for learners to get the complete picture.
Hence:
- Take your online training one notch closer to reality with simulations and move over the chalk-and-talk.
- eLearning simulations will enable your learners to be better prepared and master the skill before they apply it at work.
This eliminates costly delays and errors at work and ensures learners are more confident and hands-on. They can also think on their feet and apply knowledge in new situations.
Simulations and Experiential Learning
Simulations play a pivotal role in supporting experiential learning, bridging the gap between theory and practice. They create a safe, controlled environment where learners can engage in active experimentation without the risks associated with real-world consequences.
This hands-on approach not only reinforces learning but also builds confidence and competence as learners can fail, reflect, and try again until mastery is achieved. Additionally, simulations offer immediate feedback, allowing learners to adjust their strategies and improve their performance continuously.
Simulations primarily support the Active Experimentation phase of Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory.
2. Create Opportunities for Reflection with Scenarios in eLearning
So, you have given your learners all the information necessary to broaden their knowledge and move on to unlock professional opportunities. However, do they have the opportunity to encode and experience the eLearning content into their memory or are they merely going through the motions? It is only through reflecting and putting that knowledge into use can learners truly process the information.
How do you enable that?
- Emphasize the practical utilization of knowledge and skills that learners have acquired.
- Scenarios immerse your learners in real-life situations so that they can evaluate their responses and experience the consequences.
In case you want to raise the engagement quotient of scenarios one notch higher, you can leverage the power of branching scenarios. Much like scenarios, branching scenarios in eLearning pose challenges and seek decisions from employees. Each decision they take will lead them onto a further path. Thus, learners will immediately experience the consequences of their choices and see how they lead them to the big picture.
Scenarios play a crucial role in supporting experiential learning theory by facilitating the Reflective Observation phase. Scenarios provide realistic and immersive environments where learners can explore different responses and observe the consequences of their choices. This engagement helps them to critically assess their behaviors and decision-making processes. By analyzing the results of their actions in these scenarios, learners can explore different perspectives.

Align Training with Business Goals
Editable Questionnaire to Help You Make the Right Choice!
- Identify organizational goals
- Check what your people need to do achieve those goals
- Identify SMART learning objectives to fill performance gaps
- Design for impact
This reflective practice not only enhances comprehension but also reinforces practical skills, facilitating the transition to Abstract Conceptualization, where learners can formulate new strategies and approaches based on their insights. Through well-constructed scenarios, eLearning programs can effectively nurture learners’ ability to think critically and adaptively in real-world situations.
3. Leverage the Power of Shared Learning with Social Learning
Nowadays, social platforms are one of the easy, accessible ways to foster experiential learning. Why do you think social learning has started to become a favorite among organizations? It’s because social learning in online training allows your employees to observe, share, and imbibe knowledge from others and with others. Unlike a one-time learning event, social learning enables continuous learning.
- In the online learning framework, this can happen through the medium of blogs, discussion forums, user-generated videos, podcasts, blogs, and more.
- Social learning helps learners get access to tips and help on an on-demand basis and also share their success stories with peers, fostering experiences.
Social learning supports Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory by enhancing the Concrete Experience and Reflective Observation phases. In the Concrete Experience phase, learners engage in shared activities or discussions, providing them with immediate, tangible experiences combined with social feedback. This interaction allows learners to be immersed in a diverse range of perspectives and insights from peers, enriching their learning experience.
In the Reflective Observation phase, social learning provides a platform for learners to reflect on their experiences and observations in a collaborative setting. This reflection is deepened through dialogue with others, encouraging learners to consider alternative viewpoints and understand the implications of their actions or decisions.
Through social learning, individuals can validate their experiences and gain new insights, ensuring that learning is both personal and collective, thereby reinforcing the cycle of experiential learning.
4. Allow Experiential Learning by Exploring with Gamification
Much like the common phrase, “life would be better if it were fun,” gamification allows experiential learning, making it engaging and motivating.
Gamification in eLearning minimizes passive learning by challenging learners at exactly the right points. When learners feel challenged, they are motivated to explore and come back for more. They are wired to take pleasure from the whole process of overcoming obstacles and succeeding to move on to the next level.
Designing your eLearning courses around doable challenges makes your course more less like a one-sided lecture session. For instance, you can devise the challenge to be in many forms such as unlocking different sections of an eLearning course, or else it could be a puzzle that demands exploration and consequent solving.
Use leaderboards that display points and badges; this will infuse competition and increase the appeal of experiential learning.
Gamification in eLearning supports Kolb's Experiential Learning Theory by enhancing the Active Experimentation phase. This phase emphasizes the application of new ideas and strategies in practical contexts. Through gamification, learners are presented with challenges and tasks that require them to actively engage and apply their knowledge in a simulated environment.
Gamification elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards encourage learners to test hypotheses, explore new solutions, and experiment with different approaches. These features motivate learners to actively participate and invest effort in the learning process, as they receive immediate feedback on their actions, which is crucial for refining understanding and improving performance.
Experiential Learning and Business Goals
Integrating experiential learning into your training programs can significantly enhance the connection between training initiatives and overarching business goals. Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and real-world problem-solving, which aligns well with the practical demands of business environments.
Fostering skills such as critical thinking, adaptability, and teamwork equips employees with the tools to tackle organizational challenges effectively. This alignment ensures that the skills and knowledge acquired during training are directly applicable to the tasks and objectives employees face daily.
Moreover, experiential learning encourages continuous improvement and innovation by allowing learners to experiment, reflect, and apply lessons learned, thereby driving performance enhancements that benefit the organization as a whole.
By embedding experiential learning within training frameworks, businesses can ensure that learning outcomes are not just theoretical, but translate into tangible results that propel the company towards its strategic objectives.
Download our template to align your training with business goals. The easy-to-follow template will ensure you have everything in place. Take the next step in developing champions within your organization—download the template now and make your eLearning courses more impactful!