The Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy in eLearning and its Application

Are your training programs effective? A question most of us would ask, if we were involved in the design or delivery of training programs, be it classroom or online training. How can one design online training programs that make learners think instead of just passively going through training content? Talk to instructional designers about this and you might hear the term ‘Bloom’s Taxonomy’ being used often, especially when it comes to assessing learning and framing learning objectives.
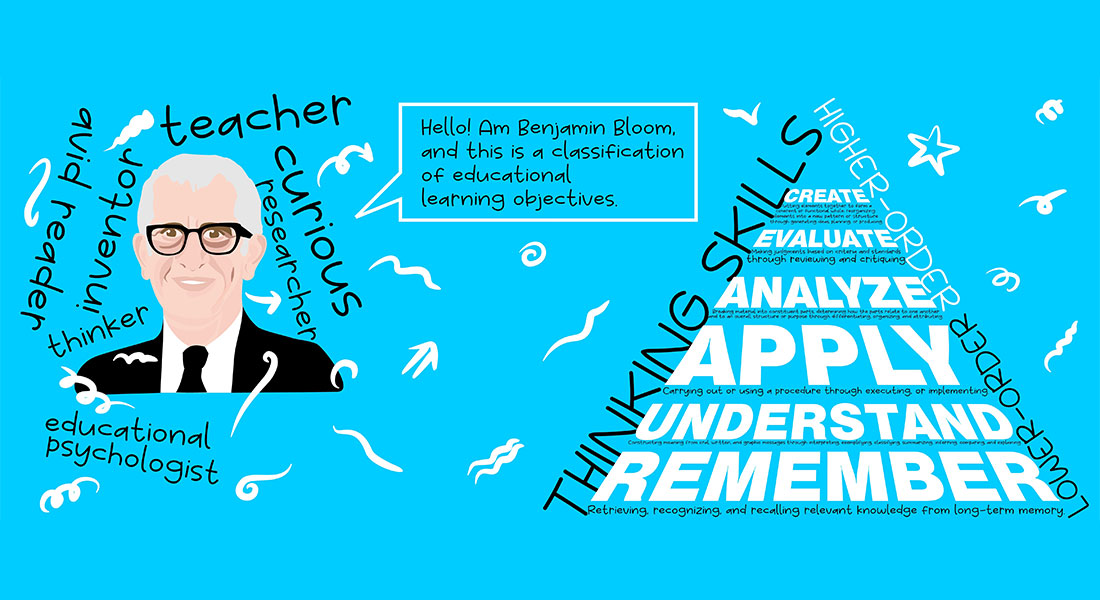
6 Levels in Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy
The popular Bloom’s taxonomy that provides a framework for designing effective training programs was revised in 2001 to make it a better fit for training techniques in the 21st century. The 6 levels in revised Bloom’s taxonomy are:
- Remembering
- Understanding
- Applying
- Analyzing
- Evaluating
- Creating
So, what exactly is Bloom’s taxonomy? Dr. Benjamin Bloom in 1956, proposed Bloom’s taxonomy which is a framework to assess learning in the cognitive domain (various knowledge and intellectual levels). The cognitive domain is further divided into 6 levels from the basic to the most complex levels of thinking, and this is what Bloom’s taxonomy covers. In 2001, Lorin Anderson revised Bloom’s taxonomy to make it a better fit to the educational techniques of the 21st century.
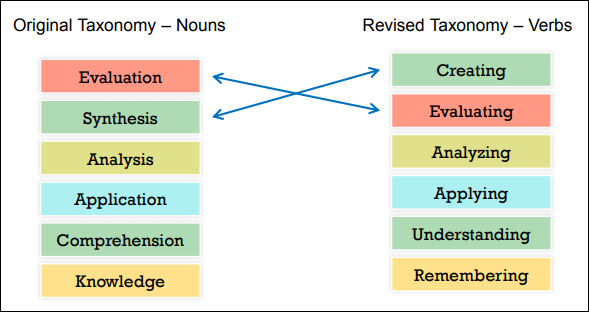
What Changed in the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy?
Here are the changes in Bloom’s taxonomy.
- As thinking is an active process, verbs are used in the revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy replacing the noun forms in the original.
- The ‘Knowledge’ level in the original Bloom’s taxonomy does not denote a level of thinking and is hence replaced by the word ‘remembering’.
- Some levels were re-organized (as illustrated below).
As training managers, having a basic understanding of what each level in Bloom’s taxonomy means and how it can be applied in e-learning can help you gain a new perspective on the way you train your employees. The 6 levels in revised Bloom’s taxonomy are as follows.
1. Remembering
This is the first level of learning and simply involves recognizing or recalling facts, concepts, or answers. List, Identify, Recognize, Find, and Locate are some of the action verbs that can be used in this level.
Example: In an e-learning course for the manufacturing industry, learners are to be taught about the working of a generator. Consider a labeled image that displays the different parts of a generator.
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Identify the different parts of a generator
- List the different parts of a generator
At the ‘Remembering’ level, you can include a hotspot activity where learners are required to click the right spot on the image of the generator depending on the part they are asked to identify.
2. Understanding
At this level, the learner grasps the information and interprets what has been learned. Some of the action verbs that can be used at this level are Summarize, Classify, Explain, Describe, and Interpret.
Example: In an e-learning course for healthcare workers, consider a video that shows learners how to perform a CPR.
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Explain the steps to perform a CPR
- Summarize the process of performing a CPR
At the ‘understanding’ level, you can use a matching activity or sequencing activity where learners have to arrange the steps to perform a CPR in the right sequence.
3. Applying
At this level, the learner must be able to apply the information that he has learned. The learner must use the knowledge gained in a new situation. Apply, Solve, Use, Demonstrate, Calculate, and Predict are some of the action verbs.
Example: In an online software training on ERP, simulations are used to show learners how to perform a specific task. Let’s say learners are to be taught how to generate a purchase order. How would you apply Level 3 of Bloom’s taxonomy in the learning objectives and assessment?
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Use the purchase order module in the ERP system to generate a purchase order
- Demonstrate the generation of a purchase order
At the ‘Applying’ level, you can include a simulation of the ERP system where a learner can practice how to generate a purchase order. Make use of ‘watch-try-do’ simulations that let learners understand how to perform a particular task in the ERP system and then practice it using simulations in e-learning.
4. Analyzing
This level of learning is where the learner breaks the information he/she has learned into parts to get a better understanding. Analyze, Compare, Attribute, Deconstruct, and Organize are some of the action verbs that can be used in objectives framed at this level.
Example: In a sales training program, learners learn about the sales process followed in different branches of the organization located across the globe.
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Analyze the bottlenecks in the sales process followed in China
- Compare the sales process followed in the USA with that of China
Activities that are based on learning objectives at this level can be time consuming, and may work better in a blended learning environment, or a collaborative learning experience where participants interact with each other on a discussion forum.
5. Evaluating
At this level of learning, you want learners to be able to make decisions through research and by thorough evaluation of options. Verbs such as Predict, Rank, Measure, Assess, and Conclude could be used to frame objectives at this level.
Example: A quality assurance training program where learners are taught how to evaluate the quality of products based on certain criteria.
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Assess the quality of the product based on the quality check process followed
- Rank products based on the difference in levels of quality
This level of learning is best handled through blended learning but can be done through a detailed e-learning program as well. At the ‘evaluating’ level, learners are required to evaluate what they have learned and take appropriate decisions.
6. Creating
At this level of learning, learners should be able to create new ideas and information using what they have learned previously. Build, Estimate, Generate, Modify, Plan, and Create are some of the verbs that can be used to frame objectives at this level.
Example: A computer language training program that teaches learners HTML5 programming.
Relevant Learning Objectives:
- Build a website using HTML5 as the programming language
- Modify a website using HTML5 to make it accessible on mobile devices
This level of learning can be achieved through a blended learning program that also incorporates the use of a discussion board or forum.
Now that you have gained an overview of revised Bloom’s taxonomy, you should be able to ensure the training programs rolled out in your organization help learners apply what they have learned. What level of Bloom’s taxonomy are you using in your current training programs? Think about the changes you could make to deliver a higher level of learning experience for your workforce.