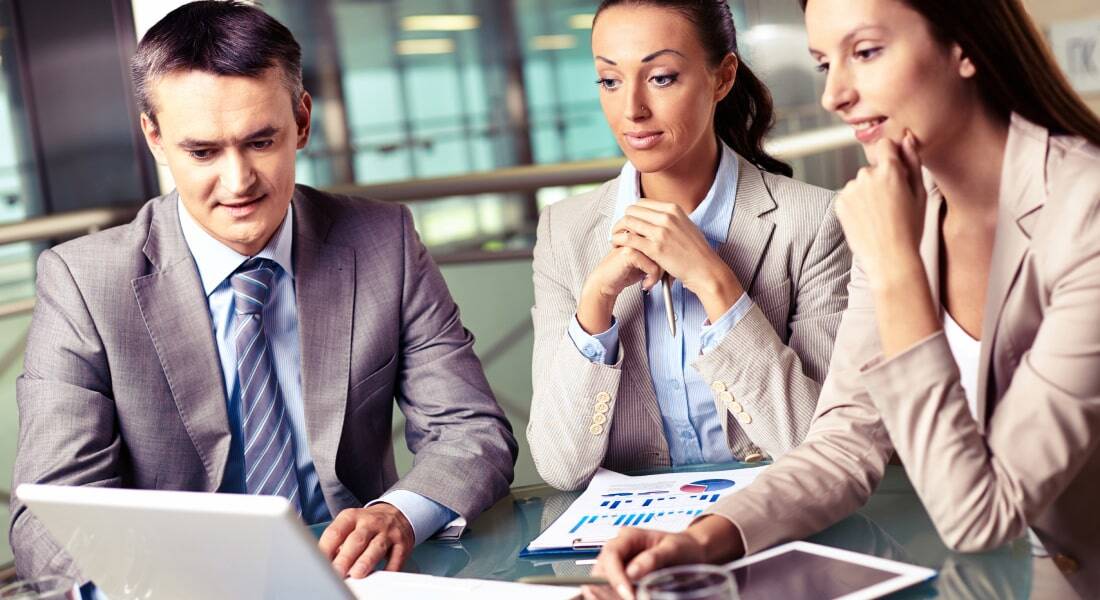
5 Effective Instructional Strategies for Experiential eLearning

Imagine learning how to ride a bicycle. No amount of reading about balance or watching others could compare to the moment you climbed onto the seat, wobbled, and pedaled forward. That’s experiential learning—learning by doing. It’s the same way many of us learned to bake cookies with a parent or solve problems during a group project in school. By actively engaging in a task, we’re not just absorbing knowledge; we’re experiencing it firsthand, building skills and confidence along the way.

This hands-on approach is at the heart of experiential learning, where action becomes the teacher. And as we grow older, this approach doesn’t change. Whether it’s landing your first job or navigating corporate training, hands-on experience remains key. By actively engaging in tasks, we don’t just gain knowledge—we build real skills, confidence, and the ability to adapt, no matter the stage of life.
Experiential eLearning remains a relatively unknown concept in the corporate sector. Nevertheless, it can prove extremely useful. Let’s explore more about it.
→ Download Now: Instructional Design 101
Table of Content
- How Experiential Learning is Redefining Corporate Training?
- What are the Benefits of Experiential eLearning?
- What Are the Best Instructional Strategies for Creating Experiential eLearning?
- How Can You Use AI Tools for Experiential eLearning?
- A Success Story you Shouldn’t Miss
How Experiential Learning is Redefining Corporate Training?
Corporate training is evolving, and experiential learning is leading the charge. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on lectures and theoretical knowledge, experiential learning immerses employees in hands-on activities, real-world scenarios, and problem-solving tasks. This approach helps individuals not only grasp concepts but also apply them in practical situations, making the learning experience more engaging and effective. By focusing on doing rather than just listening, experiential learning fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and adaptability—key skills in today’s fast-paced work environment.

Companies are increasingly adopting experiential learning because it drives better retention and results. Employees who actively participate in their learning process are more likely to recall and utilize their training in real-world applications. Whether it’s through simulations, role-playing, or project-based activities, this approach creates a deeper connection between the learner and the material. As organizations strive to stay competitive, experiential learning is proving to be a game-changer in equipping teams with the skills and confidence they need to succeed.
What are the Benefits of Experiential eLearning?
Here are some of the unique benefits of experiential eLearning for corporate training in the new normal:
1. Behavioral Change
The brick-and-mortar classroom places restrictions on employees by asking them to follow specific rules and regulations. This often limits their freedom and creativity. However, experiential learning, which often involves learning from failures, can trigger behavioral changes, during the learning phase, that helps employees overcome the obstacles holding them back.
2. Theories and Concepts Integrated with Everyday Tasks
One of the key differences between experiential training and microlearning is that the latter offers theories. In contrast, experiential learning provides concepts alongside real-world opportunities to put what employees have learned into action. A great example of experiential learning are simulations or mock courtroom trials where learners participate in the legal process rather than merely reading about it.
3. Fun and Immersive Learning Experience
Fun, curiosity, and engagement are the keys to energize one’s learning. Experiential eLearning offers more than just an immersive digital learning experience. It also enables employees to absorb knowledge by putting their learning to practice, and not just passively watching, reading, listening, or taking notes. Learners that participate in experiential eLearning can smoothen the learning curve and pick up new concepts and skills much faster than through other eLearning methods.
4. Better Retention
In the way that practice builds muscle memory, experiential learning triggers long-term behavioral change. Therefore, learners are more likely to grasp and recall information performing real-world activities instead of watching short videos or taking regular quizzes.
Providing immediate feedback can improve learners’ self-awareness, proficiency, confidence, and enthusiasm. This can also enhance retention, as you can use feedback to address misconceptions, reinforce training strategies, and boost participation.

Instructional Design 101
A Handy Reference Guide for eLearning Designers
- eLearning standards
- Streamlined instructional design process
- Effective assessments
- And More!
What Are the Best Instructional Strategies for Creating Experiential eLearning?
The Ultimate Guide to Experiential eLearning Techniques
Leverage the following instructional strategies:
- Scenario-based Learning
- Simulations
- Gamification
- Social Learning
- Immersive Technologies
1. Scenario-based Learning
Scenario-based learning is an instructional design strategy that places learners in realistic, problem-solving situations to help them apply knowledge in a practical context. By creating scenarios that mimic real-world challenges, learners can explore different solutions, make decisions, and see the outcomes of their actions in a safe environment. This approach enhances critical thinking and decision-making skills, making it ideal for experiential eLearning.
In experiential eLearning, scenario-based learning helps bridge the gap between theory and practice. For instance, customer service employees might engage in scenarios where they respond to an upset customer, choosing from various communication strategies and observing how their choices impact customer satisfaction. This method not only builds confidence but also prepares learners for similar challenges in their workplace, ensuring a smooth transition from learning to real-world application.
Similarly, a healthcare professional might work through a simulated patient scenario where they are presented with symptoms, medical history, and test results. They would then need to diagnose the condition, recommend further tests, or develop a treatment plan, receiving feedback at each step.
2. Simulations
Simulations allow corporate learners to engage with realistic, interactive environments that replicate workplace scenarios. This strategy provides hands-on experience where employees can practice skills and refine techniques without real-world risks. For example, customer service representatives can use simulations where they interact with virtual customers who exhibit challenging behaviors, such as being irate or overly demanding. They practice active listening, problem-solving, and empathy, receiving feedback on their performance. Team leaders might participate in a simulated conflict resolution exercise where they must mediate a disagreement between two virtual team members, deciding on strategies to maintain team harmony and productivity.
eLearning simulations in training are particularly effective in industries like finance, sales, and project management, where decision-making and execution are critical. For instance, in the realm of software, developers or IT professionals can use software simulations to replicate system outages or cybersecurity attacks, allowing them to practice troubleshooting, debugging, or responding to threats in a controlled environment. By mimicking workplace conditions, simulations enhance knowledge retention and ensure employees are well-prepared for their roles.
Watch this video to explore why simulations are a game-changer for employee training and development!
3. Gamification
Gamification in corporate training incorporates game elements like rewards, challenges, and leaderboards to make learning engaging and impactful. This approach motivates employees by fostering healthy competition and encouraging progress.
For example, sales teams might participate in a gamified training program where they earn badges for completing modules on sales strategies, achieving performance milestones, or closing deals in simulated environments. The program might include challenges like reaching a specific sales quota within a set timeframe, with rewards like digital trophies or advancement on a leaderboard. Employees working on compliance training might compete in quizzes where they answer questions on company policies, earning points for speed and accuracy. Leaderboards monitor progress, inspire friendly competition, and encourage participants to work on improving their performance.
These elements make learning interactive and fun while also driving participation, boosting morale, and encouraging goal achievement. For instance, gamification in leadership training might involve a virtual game where managers navigate challenges like employee retention, resource allocation, and team performance, earning rewards for effective strategies. This not only makes training engaging but also ensures practical application of knowledge in a way that resonates with employees.
4. Social Learning
Social learning focuses on collaboration and interaction among employees to encourage knowledge sharing and strengthen team dynamics. This approach allows employees to learn from each other's experiences, perspectives, and constructive feedback, fostering an environment of continuous growth and improvement. Discussions, collaborative projects, and mentorship programs are common ways to promote social learning. For example, new hires might participate in peer-mentorship programs where seasoned employees guide them through company processes, share their professional experiences, and offer practical tips to succeed in their roles. Similarly, teams can work together on problem-solving exercises during leadership workshops, exchanging ideas and approaches that not only build individual skills but also improve team cohesion. By emphasizing teamwork, open communication, and innovative thinking, social learning becomes a vital part of corporate training programs, helping organizations cultivate a culture of collaboration and adaptability.

Instructional Design 101
A Handy Reference Guide for eLearning Designers
- eLearning standards
- Streamlined instructional design process
- Effective assessments
- And More!
5. Immersive Technologies
Immersive technologies, such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), provide highly engaging and interactive learning environments for employees. These tools allow participants to dive into realistic, simulated scenarios that mimic real-world business challenges, enhancing their understanding and ability to apply skills effectively. For instance, safety officers can use AR simulations to virtually navigate hazardous workplace environments without any physical risk. In these scenarios, they might identify common dangers such as chemical spills, faulty equipment, or fire hazards and practice the appropriate safety protocols in real-time. Through repeated exposure to these simulated challenges, employees gain hands-on experience in a controlled and risk-free setting, helping them feel more confident and prepared for similar situations in their actual work environment. Immersive technologies combine the benefits of experiential learning with cutting-edge tools, making them an invaluable addition to corporate training strategies.
Explore how AR and VR are revolutionizing corporate training by creating immersive, engaging, and experiential learning experiences. Dive into the benefits and challenges in this infographic!
How Can You Use AI Tools for Experiential eLearning?
Want to make learning more immersive and engaging? AI is transforming experiential eLearning, bringing real-world simulations and interactive experiences to life like never before. AI tools for eLearning design and development are truly revolutionizing the process.
Curious how it all works and how you can use it in your eLearning strategies? Watch this video to explore the incredible possibilities AI offers for experiential learning and discover how to take your corporate training programs to the next level!
A Success Story you Shouldn’t Miss
A 2-day classroom training on creating customer offers for a new system was transformed into an engaging eLearning program. Through interactive simulations, learners gained hands-on experience with the system, empowering them to confidently create customer offers. The result? A well-trained team ready to excel.
Gain detailed Insights: Transform Sales Training with Experiential eLearning Simulations
Wrapping Up!
Understanding the evolving preferences and behaviors of employees is key to crafting impactful learning experiences. Experiential learning goes beyond traditional methods, offering a dynamic way to uncover learners’ capabilities, strengths, and areas for growth. It provides actionable insights that help tailor strategies to individual needs, fostering deeper engagement and meaningful progress.
Ultimately, experiential learning isn’t just about skill-building—it’s about driving long-term behavioral change. By creating immersive, hands-on opportunities, organizations can empower employees to unlock their potential, align with organizational goals, and thrive in an ever-changing workplace.
Now that you know how beneficial experiential learning is in corporate training, it’s time to figure out how to design it effectively. Are you interested in learning more about the instructional design process, eLearning interactivities, and assessments? Get all your queries answered by downloading this free eBook.







![All About Quiet Quitting [The Concept + Causes + Prevention + 3 Instructional Design Strategies to Rescue]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hubfs/Imported_Blog_Media/All-About-Quiet-Quitting-The-Concept-Causes-Prevention-3-Instructional-Design-Strategies-to-Rescue.jpg)