6 Crucial Stages of Prototyping Rapid eLearning Courses
W
ith the advancement of technology, the demand for rapid eLearning has skyrocketed, making it an essential part of modern corporate training. However, creating a successful rapid eLearning course is not an easy feat. It requires careful planning, designing, and testing before it can be launched to the public. This is where prototyping comes in. Prototyping allows the designers to create a working model of their eLearning course, test it, and refine it until it meets the needs of their target audience. In this rapidly changing world, where learning never stops, prototyping is crucial to ensure that rapid eLearning courses are engaging, effective, and error-free.
Struggling to Design and Deliver Flawless Rapid eLearning Courses? Start with a Prototype!
Check out the 6 crucial stages of prototyping below –
- Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Testing
- Implementation
- Evaluation
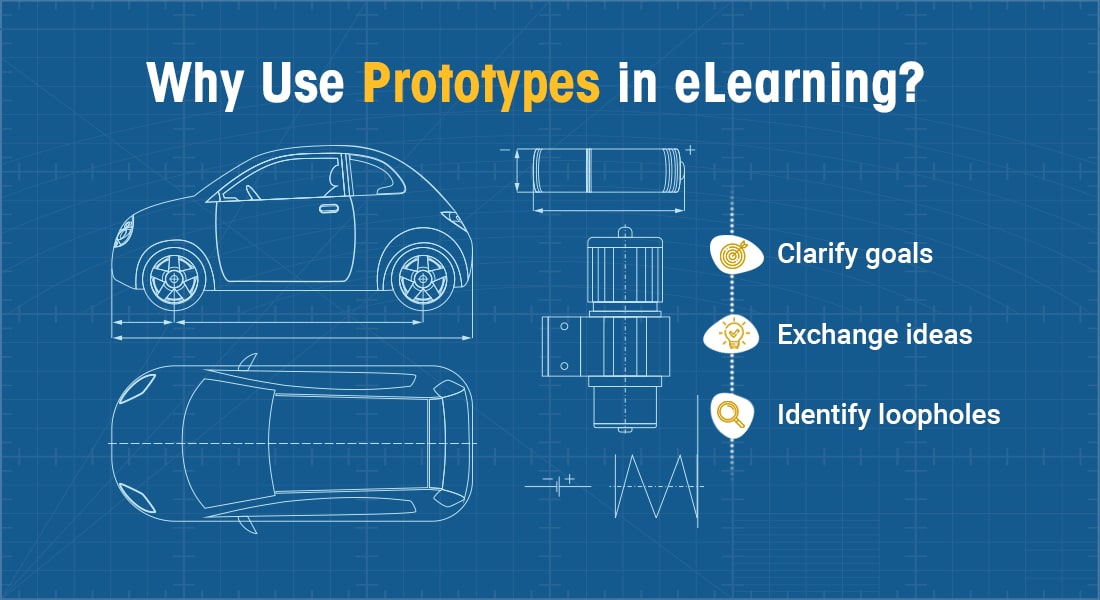
Read on to explore a few common pitfalls to avoid during prototyping.
6 Crucial Stages of Prototyping Rapid eLearning Courses
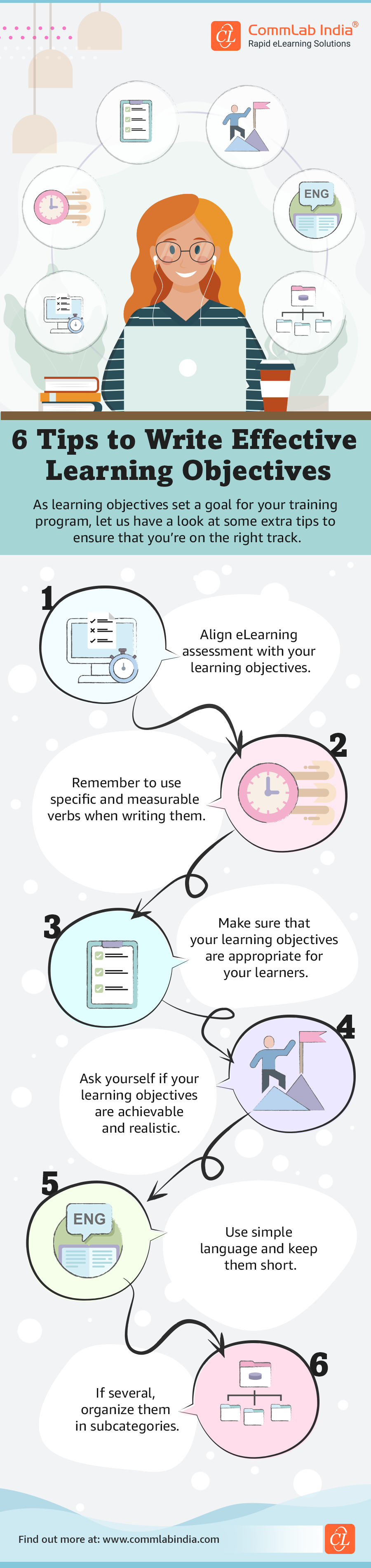
1. Analysis: In this stage, the instructional designer gathers information from the stakeholders to identify the learning objectives, target audience, learning needs, and course content. Based on this information, the designer creates a plan for the prototype.
Here's an infographic to help you get your learning objectives right.
2. Design: Here, the designer creates the prototype design by selecting instructional strategies, choosing the training format, creating storyboards and visual aids, and determining the level of interactivity.
3. Development: In this stage, the designer develops the actual prototype by creating multimedia content, graphics, and animations. The designer may also incorporate assessment tools, interactive simulations, and other instructional resources.
→Download eBook Now – Instructional Design 101
4. Testing: When the development is sorted, the designer tests the prototype with a sample audience to evaluate its effectiveness, identify errors, and make necessary revisions. The designer may use feedback from the testing phase to improve the prototype.
5. Implementation: After testing, the designer deploys the rapid eLearning course and shares it with the intended audience. This stage may also include training for instructors or administrators, if necessary. Technical issues related to the accessibility of these courses are also detected in this stage itself.
6. Evaluation: Finally, the designer evaluates the effectiveness of the rapid eLearning course by measuring learning outcomes, analyzing feedback from learners, and assessing the course’s impact on organizational goals.
Pitfalls Organizations Need to Avoid While Prototyping Rapid eLearning Courses.
1. Skipping the Analysis Stage
One of the biggest pitfalls is skipping the analysis stage or not spending enough time on it. This can lead to a course that does not meet the needs of the target audience or address the learning objectives effectively.
2. Lack of Clarity on Learning Objectives
It’s important for organizations to be clear on the learning objectives they want the course to achieve. If the objectives are not clearly defined, it may be difficult to develop effective course content and assess the effectiveness of the course.
3. Limited or No Testing
Testing is a crucial stage of prototyping eLearning design and development, but organizations may skip this step due to time or budget constraints. Without testing, it’s difficult to identify errors and make necessary revisions to the course.
4. Overcomplicating Course Content
It’s important to ensure that the course content is clear and easy to understand for the target audience. Overcomplicating the content with technical jargon or complex language can make it difficult for learners to understand and retain the information.
5. Lack of Interactivity
eLearning courses that lack interactivity can be boring and fail to engage learners. It’s important to incorporate interactive elements such as simulations, games, quizzes, and other activities to keep learners engaged and motivated.
6. Ignoring Feedback
Organizations should gather feedback from learners and subject matter experts(SMEs) after their prototypes are ready and that’s what rapid eLearning helps with. It reduces the time SMEs need to invest in providing their feedback, by deducting the total number of touchpoints. Ignoring feedback can result in a course that is ineffective or doesn’t meet the needs of the target audience.
Wrapping Up!
In conclusion, prototyping is an essential step in the development of eLearning courses. It helps to identify and fix issues early in the design process, ensures that the course content is effective and engaging, and ultimately saves a considerable amount of time for your SMEs. Apart from prototyping, there are various other ways rapid eLearning can save SMEs time and your sanity as well, wish to know them all? Check out this free webinar recording now!
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in March 2023 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.