Story Boarding Strategies for Effective eLearning

The e-learning story board is a document that shows how the content will be presented on screen. It is like a blue print of an online course. It describes every screen in a course including what learners will see and hear. It’s the plan for sequencing the content, applying a consistent style, designing meaningful activities, providing instruction to and obtaining feedback from the learners and so on.
Need for developing a story board
Most of the times, clients do not know how the course is going to look like. Story board helps them by detailing how the information would be presented and how the slides will actually look. It gives an idea about how the course will be and the client may suggest changes if he so requires. Changes made in story board save lot of time and money. For example, before constructing a house you have a specific plan and build your house according to the plan. After construction if you want three bed rooms instead of two, you would incur more costs for the rework. So changes when made at planning stage itself, saves lot of time and money. Similarly, in elearning when clients see the story board before the actual course, they can suggest changes according to the feedback provided by subject matter experts.
The basic elements of an effective story board are as follows
A story board template basically consists of four basic elements:
1. Title
It specifies the course name, unit name, slide number and slide title. Give a unique identification and clear title for the each slide that helps the course developers to put the course in correct order on one hand and enables learners to have a clear idea of what they are going to learn in that specific slide on the other. ![]()
2. Audio
Audio script, audio sync notes, instruction regarding sound effects etc. are included in this area. In audio sync area, sync notes need to be given – these are instructions as to when a particular text and image appear on screen. If there is no synchronization needed, text and image will appear simultaneously.

Pronunciation: Keys for pronouncing difficult terms are mentioned in this area. For example: for word receipt (ri-seet).

3. Interactivity Instructions
Instructions regarding interactions where learners need to complete interactivities in order to proceed to the next step or to the next slide are mentioned here. Different types of interactivities can be provided in the form of hotspots, clickable images, slide shows etc.
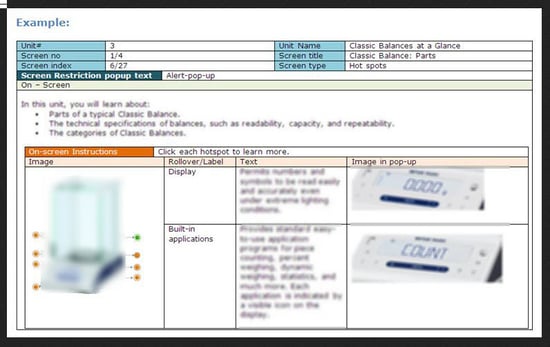
4. On screen Text
This area represents the text that appears on screen and is a part of the audio. For a particular slide if audio is used, shorter sentences are preferable. If there is no audio you may use slightly longer sentences. Using too many fonts and colors is not advisable and the text should be easily understandable to your audience. Images that need to appear on the screen are also indicated in this area. Images need to be included to facilitate the learner to understand the content. You need to ensure that images are not redundant.
Example of a story board for a particular slide

When developing the story know the audience and their needs well. View it from learners’ and trainers’ perspective, understand their needs and develop the slides accordingly. Finally, make sure that your stakeholder and subject matter experts agree on the story board before getting the final output developed.





