Awesome Instructional Design Tips for Effective eLearning

Hi there! We’ve bagged a project from a new stakeholder! We received the raw eLearning content and decided to use XYZ eLearning authoring tool. Work started with great enthusiasm. After a lot of effort, we developed a highly interactive custom eLearning course with an awesome UI design, colorful and creative Infographics and images.
A couple of days later…
The stakeholder reverted with his feedback: the eLearning course is not effective as learners are unable to grasp knowledge from it.
What do you think might be the prime reason?
Well, as mentioned at the start, the visual design is appealing, but the custom eLearning course is not effective. This leaves us with just one reason – ‘insufficient effort by instructional designers!’
Instructional designers (IDs) play an important role in designing an effective eLearning. The stakeholder might NOT be aware of how the custom eLearning course should be designed. All he/she expects is an effective (in terms of learning) and good-looking eLearning course. The instructional designer must ensure that the eLearning is effective, i.e., learning is provided to the learner and the visual design is appealing.
We’ve gathered a few tips from our expert in-house Instructional Designers. Follow them when designing your eLearning courses and ensure they facilitate effective corporate training!
Before you start designing the course:
Know your audience: Audience analysis is a fundamental step in instructional design principles and should be conducted during the first stage of project planning. To effectively communicate the purpose of your course, you need to understand your audience. Based on your learners’ profiles and experience, design the online course to meet their specific needs.
Frame effective learning objectives: Learning objectives (also called course objectives) specify what learners are expected to do at the end of the training program. They set the direction of the eLearning courses for the learners. The desired learning outcomes can be achieved only if the learning objectives are framed appropriately. In order to enhance the learning process and increase the scope for progress, an instructional designer in an instructional design program should be clear with the objective of the program. To learn how to frame effective learning objectives, refer to this ebook.
Building on Objectives: Steps to Effective Learning Content
- Develop assessments before “sourcing” content
- Ensure that the content is relevant to learners
- Prepare a detailed outline of the content
- Map the assessments to the learning objectives and the content
- Provide proper feedback
After framing the learning objectives:
Develop assessments before “sourcing” content: Many a time, instructional designers focus on creating the content once they have clear learning objectives and put the development of assessments on the back burner. This forces them to fit assessments within the ambit of the content. A major advantage of reversing this general trend and creating eLearning assessments first is that, it helps you know what you need to test. Another advantage of developing assessments first is that you get clarity about the topics the learning content needs to cover. Once you develop assessments that “match” the learning outcomes, it becomes easy to identify the topics that are necessary to complete these assessments successfully. This goes a long way in segregating the ‘need-to-know’ and ‘nice-to-know’ aspects of the learning content. For a few tips to design effective assessments, refer to this ebook.
Ensure that the content is relevant to learners: Your learners spend time to take your eLearning courses because they expect it will help them resolve their problems and enhance their productivity. So, ensure the content is relevant to the learners and they are able to apply the learning at the workplace. You can ensure that your content is relevant by mapping it to the learning objectives, using this simple matrix.

Learn how to frame assessments based on learning objectives?
Prepare a detailed outline of the content: Prepare a detailed outline of the content to provide an overview of the eLearning courses, a brief description of the target audience, and a list of modules and lessons. A sample detailed content outline is given below:
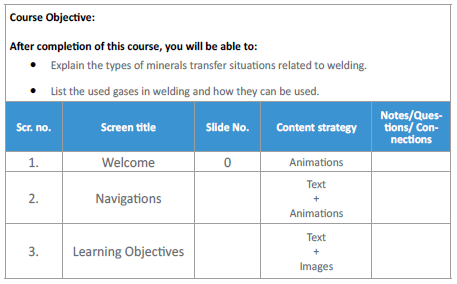
Map the assessments to the learning objectives and the content: Clearly defined objectives help you know what to expect from the eLearning courses and stay on track. They enable you to check the comprehensiveness of your eLearning courses. You can check whether the content of the custom eLearning course and the assignments meet these objectives, using this simple matrix.

Provide proper feedback: Providing feedback when the learner attempts assessments plays a prominent role. It is a very good opportunity for you to reinforce learners’ learning. So make sure the feedback you provide is proper and useful. To learn how not to give feedback, refer to this ebook.
Once you have the assessments and the content in order:
Make an interesting start: Starting your eLearning courses with the learning objectives will make it uninteresting and monotonous. There are many ways to make your eLearning courses interesting, right from the beginning. For instance, you can start your custom eLearning course with statistics about the subject being taught. This approach will help in two ways: your course starts with a “big bang” and engrosses your learners, and your learners get a gist of the subject being taught in the course.

Add videos to break monotony: Adding two-minute snippets on complicated processes or procedures facilitates a great level of interaction. Videos generate a sense of personalization and help the learner connect with your eLearning courses instantly. For more information on adding videos in eLearning, refer to this ebook.
Follow a style guide: A style guide is a document that sets the standards and ensures uniformity in style, throughout the eLearning courses. Following a style guide helps maintain consistency, avoid mistakes, and provide a better look and feel to the custom eLearning.
Allow the learner to think – use problem-based learning: The aim of any eLearning is to improve the skill/learning of the learners so that they can come up with an effective solution, when required, or perform a task correctly. So allow the learners to think and act. Use storytelling, scenario-based learning, and case-studies in your eLearning to help learners find the correct answers by themselves.
Hope you find these tips shared by our experts useful. If you wish to add, please do so through your comments.





