Essentials for Creating a Perfect Blended Learning Solution

What does it take to create a perfect blended learning solution? To create a blended learning solution, we need to know:
- What we want employees to do
- How can we help them to it
- What are the best instructional methods
These are the essential elements of creating a blended learning solution.
What we want employees to do
We expect employees to perform some tasks that will help us attain organizational objectives. A job task inventory template will help you list what you want employees to do as part of their jobs and choose the best way to help them learn to do those tasks.
Ideally, you should create a job task inventory template for each job title. Here is a description of what a job task inventory consists of:
- Job Title: Describes the overall function of the job.
- Job Duties: Identifies the broad areas of responsibilities or duties that make up the job (usually 5-8 major duties).
- Tasks: Lists the tasks that make up the broad activities to be performed on the job.
Here is a sample job task inventory template:
|
Job Title: Accountant
Date: 27th May 2017
Location: Chicago
|
|||||
| Major Job Duties | Major Tasks | Frequency | Importance | Learning | Risk |
| Research and analyze accounting data | Prepare asset, liability, and capital account entries | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Brief management of the financial status of the company, on a regular basis | Document financial transactions by entering account information | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Prepare regular reports | Prepare balance sheet, profit and loss statement, and relevant reports | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Recommend financial actions by analyzing accounting options | Reconcile financial discrepancies by collecting and analyzing account information | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| Comply with federal, state, and local financial legal requirements, and advise management on needed actions | Maintain professional and technical knowledge by reviewing professional publications; establishing personal networks; participating in professional societies | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Maintain accounting controls by preparing and recommending policies and procedures | Answer accounting procedure questions by researching and interpreting accounting policy and regulations | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Maintain financial security by following internal controls | Take regular database backups to secure financial information | 3 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
Once you have identified the job tasks, you need to categorize them based on four critical parameters:
- Frequency: Identify how often each task is performed on the job.
- Importance: Describe how important each task is to the overall effectiveness of performing the job.
- Learning: Explain how difficult the task is to learn.
- Risk: Define the risk associated with performing the task incorrectly.
It helps to rank them, so that we know how important and critical they are with respect to the main job role. Refer to the key shared below the job task analysis template to rank the four critical parameters.
How can we help them learn to do the tasks
Now that we have identified what we want employees to do as part of their jobs, we need to decide the best way to help them do those tasks. You can use one, or a combination of the following methods.
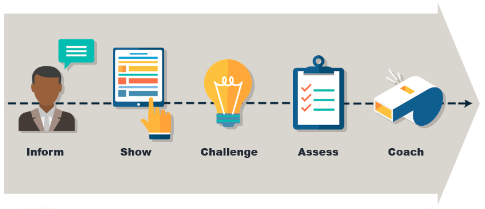
Inform: This is essential when you are presenting new information or content to employees. Examples:
- Organizational policies and procedures to new employees
- New products
- New policies or regulations
Show: You will need to practically demonstrate or simulate new information, desired knowledge or performance.
- Assembling a piece of equipment
- New safety protocol
- New software program
Challenge – Let Me Try: Here, there is a need for hands-on training, where employees get to practice with guidance, coaching, and feedback
- Assembling a piece of equipment
- Following a safety protocol
- Creating a new employee entry in the HR portal
Assess (Final Challenge): You also need to allow employees practice and provide feedback on their performance. This can be done after employees acquire a certain amount of knowledge.
- Formative assessments during training
- Summative assessments at the end of training
- On-the-job assessment
Coach: Some portion of learning will be on-the-job, in the form of performance support, as well as just-in-time learning, at the actual moment of need.
- Mentorship
- Job-aids
- Performance support
What are the best instructional methods
Once we know the different ways we can help employees learn, we need to list the different instructional methods that help us do so. Broadly speaking, the most popular ways in which employees learn today are as follows:
Formal training
- Instructor-led classroom training
- E-learning curriculum
Self-directed learning
- Microlearning modules
- E-courses
Just-in-time training
- Mobile learning
- Digital resources
Social learning
- Discussion boards
- Online forums/Wikis
Performance Support
- How-to guides/videos/job-aids
- Mobile applications
A lot of learning happens on-the-job, through peer-to-peer learning or through individual efforts of employees who try to acquire knowledge on their own. These are not listed here as they are not deliberate methods of training that organizations initiate for training.
Understanding these three elements i.e.
- What we want employees to do
- How can we help them to do it
- What are the best instructional methods
is critical to developing a blended learning solution for your organization. In the absence of this understanding, your efforts will be random, unsynchronized and aimless, with no concrete way to measure the outcome of the efforts.





