How to Design Impactful eLearning? Unveil the Secrets [Comprehensive Guide]
![How to Design Impactful eLearning? Unveil the Secrets [Comprehensive Guide] How to Design Impactful eLearning? Unveil the Secrets [Comprehensive Guide]](https://blog.commlabindia.com/hubfs/blogs/elearning-impactful-design-aspects-info.jpg)
The ability to learn anytime, anywhere, at your own pace, and in a way that truly resonates with you. That's the magic of eLearning! In today's fast-paced world, where flexibility and accessibility are key, eLearning has emerged as a powerhouse for driving learning outcomes and skill development. eLearning opens up a world of learning possibilities for professionals looking to improve their skills. And learner engagement serves as a vital aspect for the effectiveness of eLearning initiatives. Let's learn more in this blog!
→ Download Now: Instructional Design Strategies [eBook]
Table of Contents
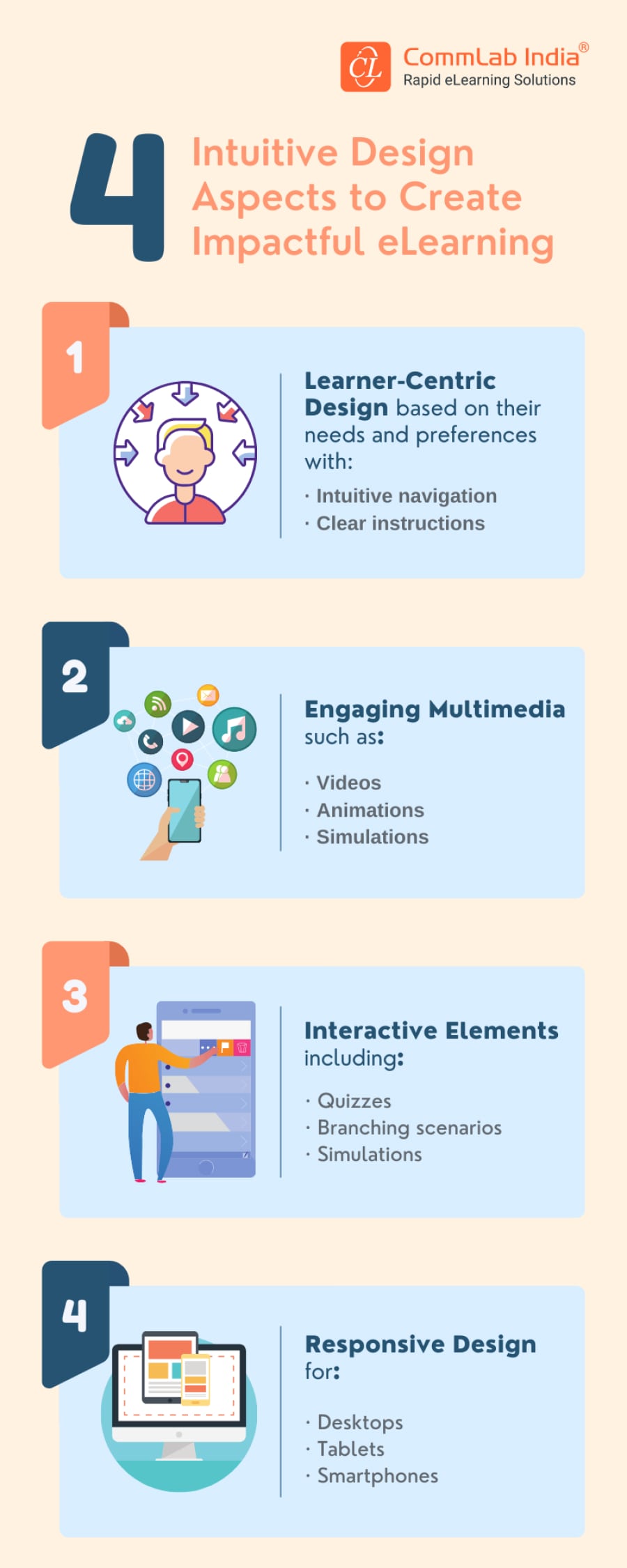
- What are the Design Aspects to Create Impactful eLearning?
- How to Amp-up eLearning Engagement?
- How to Design eLearning Courses to Boost Learner Engagement?
- What are the Multimedia Principles to Know to Design Interactive Courses?
What are the Design Aspects to Create Impactful eLearning?
How to Amp-up eLearning Engagement?
1. Make eLearning a Priority
Emphasize the importance of eLearning within the organization by aligning it with strategic goals and priorities.
Communicate the benefits of eLearning to learners, such as flexibility, accessibility, and self-paced learning opportunities.
Create a supportive learning culture that encourages participation and acknowledges the value of continuous learning and skill development.
2. Incorporate eLearning into Performance Assessment
Link eLearning initiatives with employees' performance goals and development plans to emphasize their relevance and importance.
Incorporate online learning assessments that directly contribute to performance metrics or competencies assessed during performance reviews.
Provide opportunities for learners to apply newly acquired knowledge and skills in their work context, demonstrating the practical value of eLearning.
3. Tailor and Personalize eLearning Experiences
Customize eLearning experiences to individual learners' needs, preferences, and skill levels by offering personalized learning paths or adaptive content recommendations.
Use learner data and feedback to customize the difficulty level, pacing, and content of eLearning modules to match each learner's proficiency and learning objectives.
Provide opportunities for learners to set goals, track progress, and receive personalized feedback and recommendations for improvement.

Instructional Design Strategies to Design Engaging eLearning Courses
Design Learner-Centric eLearning
- Importance of ID Strategies in eLearning
- Parameters to Select the Right ID Strategy
- ID Strategies for Effective Results
- Case Studies
4. Offer Variety in eLearning
Offer a variety of learning formats and delivery methods, including videos, interactive modules, microlearning modules, gamified courses and more to cater to diverse learning styles and preferences.
Encourage active learning by combining different formats within a single eLearning course, such as incorporating interactive quizzes, discussions, and animations.
Allow learners to choose the format or mode of learning that best suits their learning preferences, schedules, and learning objectives.
5. Evaluate the Impact of eLearning
Implement robust evaluation methods to assess the effectiveness of eLearning initiatives in achieving learning objectives and driving performance improvements.
Use learning analytics and data-driven insights to track learner progress, engagement levels, and knowledge retention throughout eLearning courses.
Solicit feedback from learners to gather insights into the perceived value and impact of eLearning on individual and organizational performance.
To ensure your eLearning courses truly resonate with learners and maximize engagement, it's crucial to employ effective design strategies. After exploring the foundational aspects of impactful eLearning and how to boost overall engagement, let's dive into specific tips to design eLearning courses that captivate and motivate learners.
How to Design eLearning Courses to Boost Learner Engagement: Tips
1. Mix and Match Different Learning Formats
Not every learner consumes information in a similar way. So, incorporating different learning formats is a powerful strategy for improving learner engagement in corporate training. When learners are exposed to a variety of learning formats, they are more likely to stay engaged and motivated to learn. You can also incorporate interactive elements, such as gamification, scenario-based learning, simulation, etc., into your training program to add variety and keep your learners engaged.
Additionally, you can use multimedia resources such as videos, podcasts, and interactive PDFs to introduce new concepts and ideas in a more dynamic and engaging way. By offering a mix of different learning formats, you can cater to the diverse learning preferences of your learners and create a more personalized and effective learning experience. Therefore, integrating a variety of learning formats into your training program ensures immersive, engaging, and interactive eLearning courses. So, it is highly recommended to include diverse learning formats for better learner engagement.
2. Leverage Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
Motivation is an important psychological factor that initiates engagement and response among learners! It can result from various reasons and outcomes. Maybe a big promotion, personal interest in a particular topic or skill development, rewards, gifts, etc. So, you can tap into the potential of internal and external motivation and leverage it to design and develop more interactive, learner-oriented eLearning courses that will boost learner engagement.
Intrinsic motivation refers to the learners’ internal drive to learn and grow, while extrinsic motivation is driven by external factors such as rewards or recognition. It helps motivate the learners to participate and achieve their learning objectives, thereby enhancing the training ROI. You can use intrinsic motivation by highlighting the personal benefits of the training and encouraging the employees to set their personal learning goals. At the same time, you can leverage extrinsic motivation by offering rewards or incentives for learners who demonstrate exceptional progress and achievement.
By using a combination of both, you can design a more holistic and effective approach to learner engagement.
What Are the Key Steps in Setting Learning Objectives?
3. Facilitate Response from the Learners
Imagine being in a situation where you are on the receiving end of the communication. It goes on and on with no participation required from your side. What would happen? It’s pretty obvious that you’ll be inattentive and eventually lose interest. Whereas, if you were expected to participate in communication or interaction, you would certainly be more alert and active. Therefore, they are more engaged and motivated.
Same is the case for your learners. So incorporating elements that seek responses from the learners in your eLearning courses is essential in maintaining learner engagement. It helps to involve and engage with the training content. You can include activities such as quizzes, polls, surveys, and even formative assessments, which allow learners to self-assess their understanding of the material. Moreover, it will benefit you in tracking their progress and addressing any areas of confusion or misunderstanding. So, designing participation-friendly, interactive eLearning courses is integral to ensuring learning engagement.
4. Incorporate Collaborative Learning
While individual learning has its merits, the presence of a companion or a group significantly enhances the learning experience, making it more efficient and engaging. This is the essence of collaborative learning. It encourages learners to work together towards a common goal or complete tasks and assignments collectively.
Collaborative learning is an effective strategy for engaging learners as it fosters active participation, promotes peer-to-peer interaction, and enables knowledge sharing among participants. By integrating collaborative learning activities into your training program, you can create a more interactive and immersive learning environment. This approach not only maintains learner motivation and focus but also enhances teamwork and cooperative skills.
Effective methods to facilitate collaborative learning include group discussions, team-based projects, breakout room activities, and interactive gaming challenges. Incorporating these strategies can significantly enrich the learning experience and contribute to the development of essential collaborative skills.

Instructional Design Strategies to Design Engaging eLearning Courses
Design Learner-Centric eLearning
- Importance of ID Strategies in eLearning
- Parameters to Select the Right ID Strategy
- ID Strategies for Effective Results
- Case Studies
5. Solicit Learner Feedback
Feedback is like a mirror to your efforts. It helps you realize the strengths and shortcomings of your corporate training. By actively soliciting feedback, you can gather valuable insights into what’s working well and what’s not and use this information to make necessary adjustments to your training program. There are several ways you can gather feedback from learners, such as through surveys, focus groups, or one-on-one discussions. You can also use technology such as learning management systems (LMS) to gather feedback in real time and make adjustments on the fly. By regularly soliciting feedback from learners, you can ensure that your training program is meeting their needs and expectations and keeping them engaged and motivated to learn.
Multimedia plays a key role in enhancing eLearning engagement! To effectively incorporate multimedia into your courses, it's essential to understand the key principles that guide its use. Let’s explore these multimedia principles to design interactive and engaging eLearning experiences.
What are the Multimedia Principles to Know to Design Interactive Courses?
1. Redundancy Principle
The Principle: People learn better from graphics and narration than from graphics, narration and onscreen text.
Some e-learning courses have text on the screen and narration in the background. This might look like a good way to present information, but it does not work. In fact, studies conducted by Mayer and others indicate that better transfer of learning happens when graphics are explained by audio alone, rather than with both audio and text. In such a case, the onscreen text becomes redundant.
When visuals and onscreen text are used together, it presents a sensory overload to the learner, because he must simultaneously understand the graphic and read the onscreen text. The reason for this is learners can process only one thing at a time. They cannot pay attention to both onscreen text and graphics, simultaneously. So, if only audio narration is added, learners process the information through their ears and focus on the graphics with their eyes. However, when there is no other visual content on the screen, research says, it is better to present the content as both text and narration, for better retention.
2. Modality Principle
The Principle: People learn better from graphics and narration than from animation and onscreen text.
Though the Modality principle may sound similar to the Redundancy principle, it is not. According to Mayer, “…put words in spoken form rather than printed form whenever the graphic (animation, video, or series of static frames) is the focus of the words and both are presented simultaneously.”E-Learning and the Science of Instruction by Ruth C. Clark & Richard E. Mayer (2016).
The Modality principle states that e-learning courses that contain graphics, must have an audio script explaining the graphics, rather than onscreen text. When graphics and audio are combined to present information, graphics are processed by the visual channel of the learner and audio is processed by the auditory channel.
If complex graphics and familiar words are presented together on the screen at a rapid pace, the learner’s attention gets dissipated and he will not be able to learn effectively.
There are certain exceptions to using onscreen text when:
You cannot record your narration or cannot afford the cost of outsourcing it
You face technical constraints of having an audience who will be using devices without audio capability
You have an audience of learners who will find it difficult to process spoken words
You have exercises in your course that require your learners to refer to the instructions
You have screen simulations which require a mixture of text, audio, and visuals
Section 508 Compliance: Including onscreen text is important when the course has to be Section 508 compliant. In such a case, use the closed captioning option or add a Notes field in the menu option that will display the text as it is narrated. This will help learners with hearing impairments.
3. Coherence Principle
The Principle: Learning is better when extraneous words, pictures and sounds are not included in the course.
Some instructional designers tend to go overboard when it comes to including graphics, illustrations, videos, and sounds in the course. Their aim is to present content in multiple dimensions so that it is easily comprehended by the learner. However, the opposite happens and they fail in their endeavor. The sensory overload that results from using extraneous pictures, visuals, text, and sounds will create a cognitive overload and confuse the learner.
Mayer conducted experiments on learners who were presented with basic details and another set which was presented with extraneous details on the same course. On assessing the 2 groups, he found out that those presented with basic details fared much better and showed better learning than the other set.
Research on why learners fail to learn effectively when presented with extraneous details, concluded that details distract learners from the core information in the course. Such details prevent the learner from organizing the material into coherent knowledge, or activate irrelevant prior learning that diverge his focus from the course. Visuals or text not relevant to the instructional explanation are best avoided.
Music at the beginning of the course to evoke learner interest and sounds for right and wrong answers in assessments are admissible, while any other sounds are extraneous.
The base rule of this principle is ‘less is more’, when the primary motive is learning.
4. Signaling Principle
The Principle: Learning is better when there are cues that highlight the critical elements of the course.
This principle states that the use of visual, auditory, and progressive cues helps to draw attention to critical elements of the lesson. To quote Mayer, “People learn better when cues that highlight the organization of the essential material are added.”
Imagine presenting your learners with a large block of text on the screen; do you think they would go through the whole text? You are right if you guessed ‘no’. Learners are intimidated by large chunks of text on the screen. If the same text is broken down into smaller chunks, and headings and images are used, then it becomes more appealing to the learner. Other ways to do this is by including illustrations, arrows, circles, highlighting or using bold format to emphasize important text, line work, or even using whitespace that can increase visual appeal.
In narration, this can be applied as pauses or vocal narration.

Using the signaling principle helps to direct the vision of the learner to certain areas on the screen and the use of cues helps him to follow a natural path that guides him through the course.

Instructional Design Strategies to Design Engaging eLearning Courses
Design Learner-Centric eLearning
- Importance of ID Strategies in eLearning
- Parameters to Select the Right ID Strategy
- ID Strategies for Effective Results
- Case Studies
5. Personalization Principle
The Principle: Learning is better when words used in the narration are in conversational style rather than a formal style.
The Personalization principle states that the learner will be engaged if first and second person narrative is used, rather than formal language. When the narration directly addresses the learner, he establishes a connection with the course.
Mayer says, “Based on cognitive theory and research evidence, we recommend that you create or select e-Learning courses that include some spoken or printed text that is conversational rather than formal.”
Other research studies on this topic recommend the use of a learning agent such as a character or an avatar, who speaking in a formal style, can improve learning.

Using the Personalization principle promotes learner engagement. When you are conversing with someone, you are expected to listen and respond. The same rule applies when the learner is interacting with the course, he has to invest his attention, process the information, and generate a meaningful response.
However there are certain caveats to this principle, you cannot overdo the first and second person constructions when writing the script for your course. Too much of a formal style can distract from the seriousness of the content. Remember, personalization is no excuse to use slang or sloppy language. The rule is to follow a conversational style, but maintain a professional tone.
Wrapping It Up
In the dynamic world of eLearning, the effectiveness of training programs hinges on both engagement and design. By incorporating diverse learning formats, leveraging intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, and facilitating interactive and collaborative learning experiences, you lay the groundwork for impactful and engaging courses. Furthermore, understanding and applying multimedia principles—such as the Redundancy, Modality, Coherence, Signaling, and Personalization principles—enhances the learning experience, making it more interactive and effective.
As eLearning continues to evolve, embracing these strategies ensures that learners remain engaged, motivated, and equipped with the skills they need to succeed.
Ready to elevate your eLearning design? Download our eBook: Instructional Design Strategies and start transforming your courses today!
Editor’s note: This post was originally published on April 18, 2024 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.